What Is IT Architecture?
Information Technology (IT) architecture is a structured framework that defines how an organization’s IT systems, software, hardware infrastructure, networks, and processes are designed and integrated to support its strategic goals. It serves as a “roadmap” to align technology with business needs while ensuring optimal consistency, scalability, and security.
In simpler terms, IT architecture organizes and standardizes an enterprise’s technology components to maximize efficiency and minimize the risks associated with the growing complexity of modern systems.
Why Is IT Architecture Crucial?
Alignment with Business Goals
IT architecture ensures that technology investments directly support the company’s strategic priorities, such as revenue growth, improved customer experience, or product innovation.
Managing Complexity
As organizations adopt new technologies, systems can become increasingly difficult to manage. A well-designed IT architecture simplifies this complexity by providing a unified, organized view of how components interact.
Scalability and Flexibility
Effective IT architecture anticipates future needs, allowing the organization to quickly adapt to market changes or new technological requirements without sacrificing performance.
Security and Compliance
IT architecture includes strategies to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR or ISO 27001. This reduces the risk of security breaches and legal penalties.
Cost Optimization
By centralizing and streamlining technology resources, IT architecture helps avoid redundancy, inefficiencies, and unnecessary spending—while maximizing return on investment (ROI).
Enabling Innovation
A well-thought-out IT infrastructure allows businesses to quickly integrate new solutions like advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, or automation—helping them stay competitive.
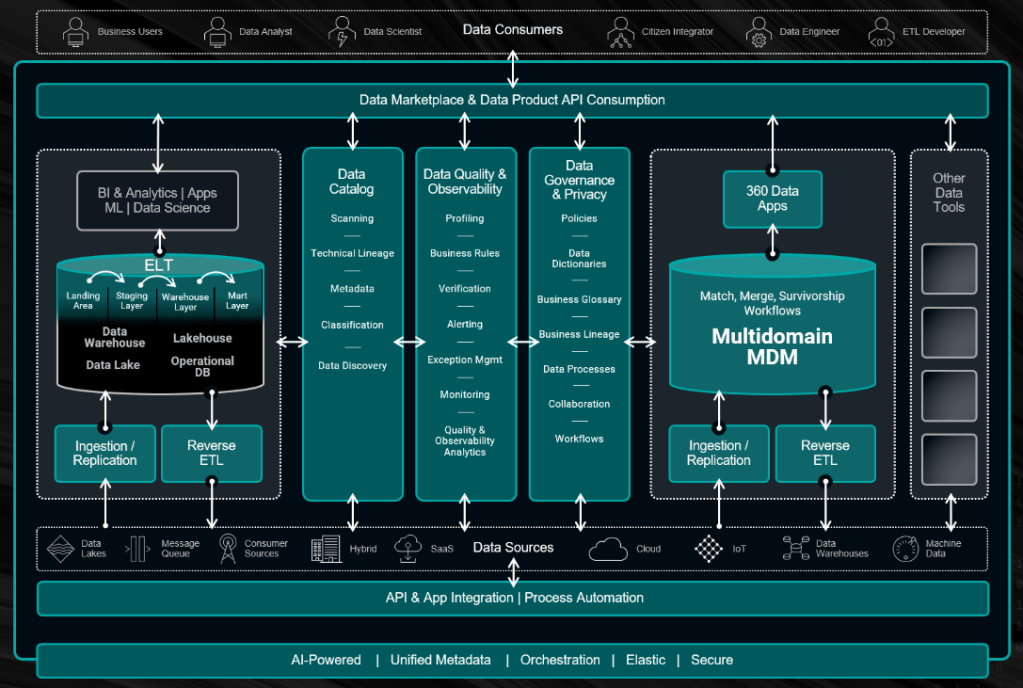
Practical Examples
- Cloud Computing: IT architecture may include a hybrid or multi-cloud strategy to ensure flexibility and resilience.
- Data Management: Architectures centered around data lakes or data warehouses help manage large-scale data (Big Data) for analysis and decision-making.
- Cybersecurity: IT architecture incorporates protection mechanisms such as zero trust models or advanced firewalls to safeguard digital assets.
Conclusion
IT architecture is not just a technical concern—it is a strategic pillar that supports digital transformation and long-term sustainability. It plays a vital role in how organizations leverage technology to innovate, differentiate, and thrive in an ever-evolving environment.
